Have you ever wondered how engineers, designers, and architects bring their ideas to life? The answer lies in a crucial skill: understanding and representing objects from multiple perspectives. This isn’t just about creating cool 3D drawings; it’s about communicating a clear, precise vision that translates into tangible results. These perspectives, often referred to as top view, front view, and side view, are foundational to fields like engineering, architecture, and even video game design.
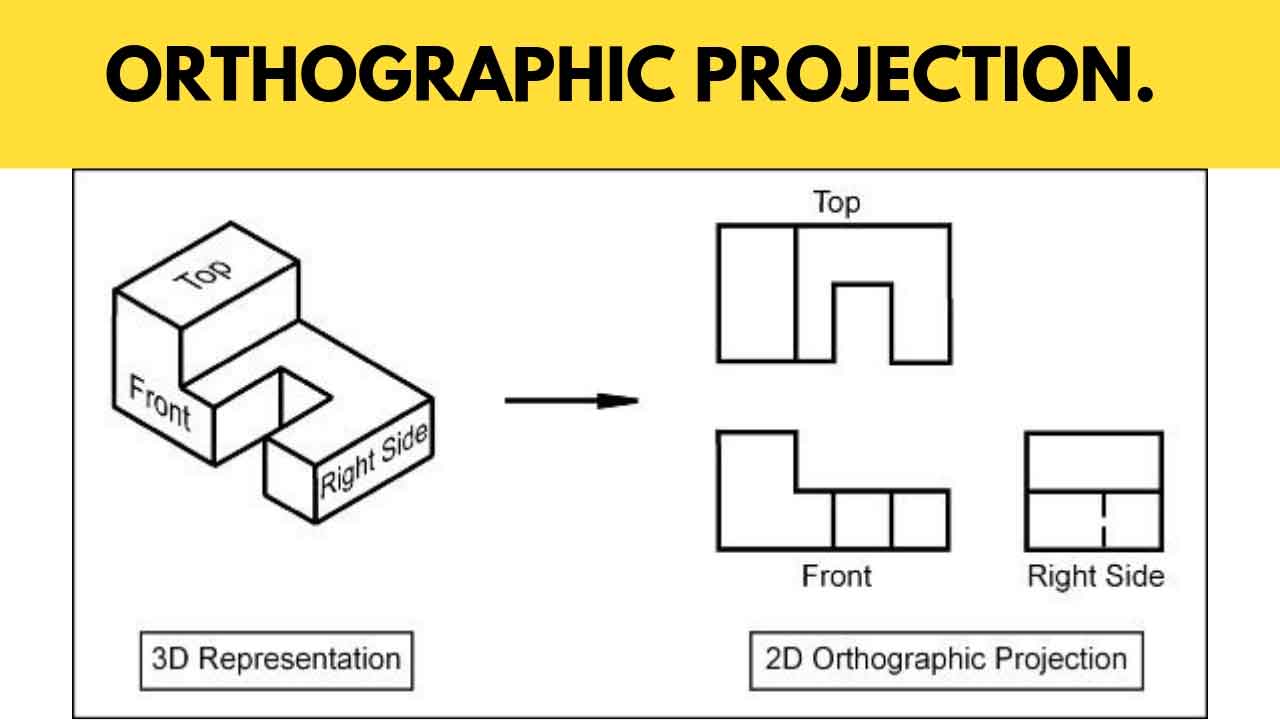
Image: skill-lync.com
This article explores the world of top, front, and side views, delving into their history, their applications, and how they revolutionize our understanding of objects. Join us as we unveil the powerful language of visual communication and discover how these perspectives shape our technological world.
The Origins of Top, Front, and Side Views: A Journey Through Time
The concept of representing objects from multiple angles can be traced back to ancient civilizations. Early cave paintings and hieroglyphs depict rudimentary representations of animals and objects, foreshadowing the development of more sophisticated methods. It was during the Renaissance, with the rise of scientific inquiry and artistic innovation, that these views took on a more formalized structure. Leonardo da Vinci, a master of both art and science, employed meticulous drawings and sketches to visually convey his understanding of the human body, machines, and the natural world. These sketches often incorporated multiple perspectives, laying the foundation for the modern principles of technical drawing.
The 18th and 19th centuries saw further advancements in engineering and architecture, demanding more precise and standardized ways of communicating designs. The development of orthographic projection, a technique that uses parallel lines to represent objects from different views, significantly shaped the field of technical drawing. This method, which is still widely used today, emphasizes the top, front, and side views, providing a complete understanding of an object’s dimensions, shape, and features.
Unveiling the Perspectives: Top, Front, and Side Views Defined
Top view, front view, and side view are three fundamental orthographic projections that create a blueprint of an object. Each view reveals a specific aspect, allowing for a comprehensive representation:
- Top View: As the name suggests, this view showcases the object as if looking down from directly above. Imagine a bird’s-eye perspective. The top view provides critical information about the object’s overall shape, dimensions, and any features that extend horizontally.
- Front View: This view presents the object as seen from the front, simulating a person standing directly in front of it. It reveals the object’s height, width, and any vertical features. The front view is often considered the primary or reference view, providing a clear outline of the object’s main form.
- Side View: The side view, as its name implies, shows the object from the side. It provides valuable insights into the object’s depth, any features that extend horizontally, and the relationship between the front and back portions.
The Power of Perspective: Real-World Applications
Top, front, and side views are not merely theoretical constructs; they are indispensable tools in various fields. Their applications are as wide-ranging as the objects they represent, influencing everything from the design of buildings to the creation of virtual worlds.
![[DIAGRAM] Software Engineering Diagrams Tutorial - MYDIAGRAM.ONLINE](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/Sxuyp7gf9DU/maxresdefault.jpg)
Image: mydiagram.online
Engineering: Building the Foundation of Our World
Engineers rely heavily on these views for designing everything from simple machines to complex bridges and skyscrapers. Imagine building a house without a blueprint – it would be a chaotic mess! Orthographic projections provide a clear guide, outlining the dimensions, materials, and relationships between different parts of the structure. These views also facilitate collaboration among engineers, ensuring that everyone is working from the same visual understanding.
Architecture: Constructing Spaces That Inspire
Architects utilize front, side, and top views to create detailed plans for buildings and structures. They carefully consider the exterior appearance, interior layout, and structural details, all meticulously represented using these perspectives. These views allow them to visualize the flow of space, natural light, and aesthetic elements, ensuring the final design meets both functional and aesthetic requirements.
Product Design: Bringing Innovation to Life
Product designers depend on these views to create detailed drawings and prototypes for everything from consumer electronics to furniture. By representing the product from various angles, they can accurately convey the form, functionality, and user experience. These views are crucial for manufacturing and production, ensuring that the final product aligns with the initial design intent.
Video Game Design: Creating Immersive Worlds
In the realm of video games, these perspectives are fundamental for creating realistic and engaging environments. Game designers use top, front, and side views to map out the layout of levels, define the placement of characters and objects, and plan the player’s movement within the virtual world. The accuracy and clarity of these projections ensure a smooth and enjoyable gaming experience.
Beyond the Basics: Advanced Techniques and Software
While the fundamental principles of top, front, and side views remain consistent, technological advancements have introduced a range of tools and techniques to enhance the process of creating these perspectives. Computer-aided design (CAD) software has revolutionized the field, enabling designers and engineers to create complex 3D models with ease. CAD software streamlines the creation of orthographic projections, automating the generation of multiple views from a single model.
Additionally, tools like isometric projection and perspective projection offer more realistic visual representations, enhancing the overall understanding of the object. Isometric projection maintains parallel lines to create a sense of depth, while perspective projection simulates the way our eyes see a scene, using converging lines to create greater realism.
The Future of Perspective: The Role of Virtual Reality and Augmented Reality
With the advent of virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR), the way we experience and interact with objects and designs is evolving. These technologies have the potential to revolutionize the way we use top, front, and side views. Imagine being able to walk through a virtual design of a building, experiencing the space firsthand, or overlaying a 3D model onto a real-world location, seeing how a structure would fit in its environment. VR and AR technologies are poised to create immersive experiences that enable us to better understand and interact with objects in a more intuitive and engaging way.
Top View Front View Side View
Conclusion: A Foundation for Understanding and Innovation
From ancient art to modern technology, understanding top view, front view, and side view is fundamental to visualizing, communicating, and creating both the tangible and the virtual. These perspectives act as a universal language, enabling different fields to collaborate and innovate. As technology continues to evolve, these views will continue to play a vital role in shaping our understanding of the world and the objects within it. Whether you are a budding architect, an aspiring engineer, or simply curious about the world around you, appreciating the power of these perspectives opens doors to a deeper understanding and a future filled with innovation.






