Imagine you’re the head chef of a bustling restaurant, tasked with crafting a delectable menu for your patrons. You have limited resources – a small kitchen, a specific set of ingredients, and a finite amount of time. With these constraints, you must carefully choose what dishes to offer, balancing quality, variety, and efficiency. This scenario mirrors the fundamental concept in economics known as the “production possibilities frontier,” which illustrates the trade-offs inherent in resource allocation.

Image: ar.inspiredpencil.com
This article delves into the creation of production possibilities schedules and curves, providing a comprehensive understanding of how these tools help visualize and analyze economic possibilities. By exploring the relationship between limited resources and potential outputs, we can gain valuable insights into economic decision-making processes, resource management, and ultimately, maximizing societal well-being.
Understanding Production Possibilities Schedules
Definition and Purpose
A production possibilities schedule (PPS) is a table that outlines the various combinations of two goods or services an economy can produce, assuming full utilization of all available resources and technology. It serves as a starting point for constructing the production possibilities curve, a graphical representation of these combinations.
Each row in a PPS represents a different production scenario, indicating the maximum amount of one good that can be produced given a specific level of production for the other good. The table showcases the trade-offs involved in resource allocation, highlighting the fact that producing more of one good necessitates producing less of another. This concept, known as opportunity cost, lies at the heart of the PPS.
Building a Production Possibilities Schedule
Constructing a PPS involves identifying the following key elements:
- Two Goods or Services: The PPS focuses on the production of two goods or services, allowing for a clear visualization of the trade-off between them.
- Resources: Define the available resources, including labor, capital, land, and technology. These resources are assumed to be fixed and fully utilized.
- Production Levels: Identify the different levels of output for each good that can be produced with the available resources. This involves considering different allocation strategies, where resources are shifted between the production of the two goods.
- Opportunity Cost: For each production scenario, calculate the opportunity cost of producing one more unit of one good. This represents the amount of the other good that must be sacrificed.
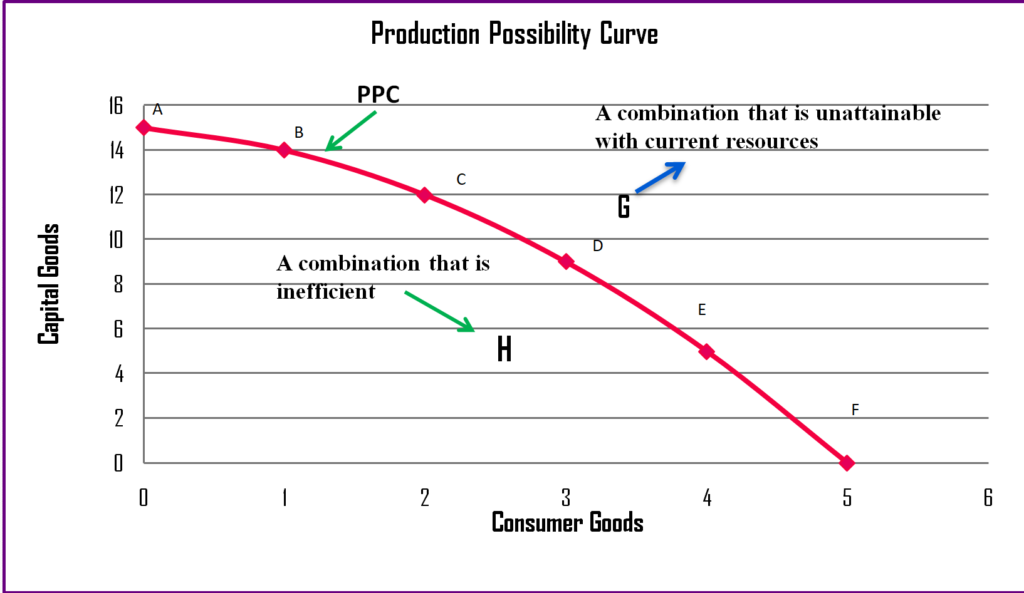
Image: enotesworld.com
Example: A Simple Production Possibilities Schedule
Let’s illustrate with a simple example of a hypothetical economy producing two goods: bicycles and cars. In this scenario, we assume the economy has limited labor and capital resources. The following table shows a hypothetical PPS:
| Bicycles | Cars |
|---|---|
| 0 | 5 |
| 10 | 4 |
| 20 | 2 |
| 30 | 0 |
From this PPS, we can see that if the economy produces no bicycles, it can produce a maximum of 5 cars. However, to produce 10 bicycles, the economy must reduce car production to 4. This demonstrates the principle of opportunity cost – the production of one good comes at the expense of another.
Visualizing Potential: Production Possibilities Curves
From Table to Curve
The production possibilities curve (PPC) is a graphical representation of the production possibilities schedule. It depicts the maximum combinations of two goods or services that an economy can produce, given its current resources and technology.
The curve is drawn with the quantity of one good on the x-axis and the quantity of the other good on the y-axis. Each point on the curve represents a specific combination of output, and these points correspond to the data points from the production possibilities schedule. The PPC typically has a concave shape, reflecting the law of increasing opportunity cost.
Key Features of the Production Possibilities Curve
The PPC possesses several key features that highlight important economic principles:
- Points Inside the Curve: Points inside the curve represent combinations of output that are achievable but inefficient. The economy is not fully utilizing its resources.
- Points on the Curve: Points on the curve represent efficient combinations of output, indicating that all resources are fully utilized. This is the maximum output possible with existing resources.
- Points Outside the Curve: Points outside the curve represent combinations of output that are currently unattainable with existing resources and technology. Achieving these points requires an increase in resources or technological advancements.
- Concavity: The concave shape of the PPC reflects increasing opportunity cost. As we produce more of one good, the opportunity cost of producing additional units of that good increases, leading to a steeper slope along the curve.
Impact of Changing Resources and Technology
Changes in resource availability or technological advancements can shift the production possibilities curve. An increase in resources or an improvement in technology can lead to an outward shift, expanding the production possibilities frontier and increasing the potential output of both goods.
Conversely, a decrease in resources or a decline in technological progress may cause the PPC to shift inward, contracting the production possibilities frontier and reducing the potential output.
Applications and Relevance
Production possibilities schedules and curves serve as powerful tools for understanding economic principles and guiding decision-making in various contexts. Some key applications include:
- Resource Allocation: The PPC helps visualize the trade-offs involved in allocating limited resources between different sectors of the economy. Policymakers can use this information to make informed decisions about resource allocation, prioritizing sectors based on societal needs and priorities.
- Economic Growth: The PPC provides insights into economic growth potential. By understanding the factors that influence the shape and position of the curve, policymakers can identify strategies to promote economic growth through increased resource availability or technological advancements.
- International Trade: PPCs are used to illustrate the benefits of international trade. When countries specialize in producing goods and services where they have a comparative advantage, they can produce more goods and services overall, resulting in higher standards of living.
- Consumer Choice: The concept of opportunity cost, visualized through the PPC, helps individuals make informed choices about their consumption patterns. By considering the trade-offs involved, consumers can allocate their resources to maximize their satisfaction.
Expert Tips and Advice
Understanding production possibilities schedules and curves can enhance your economic literacy and decision-making processes. Here are some tips to help you leverage this knowledge effectively:
- Practice: Construct production possibilities schedules and curves for different scenarios to solidify your understanding. Experiment with changes in resource levels or technology and observe how these changes affect the curve.
- Real-World Applications: Connect the concepts to real-world examples. Consider how production possibilities analysis can be applied to decisions about healthcare, education, infrastructure, or environmental conservation.
- Critical Thinking: Use the PPC as a tool for critical thinking about economic issues. Challenge assumptions, analyze trade-offs, and consider different perspectives on resource allocation dilemmas.
- Stay Informed: Keep up with the latest economic trends and developments. Understand how changes in technology, resource availability, and global events can affect production possibilities and economic growth.
By actively engaging with these concepts and applying them to practical situations, you can develop a deeper understanding of economic principles and their implications for individual choices and societal decisions.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Can the production possibilities curve ever be a straight line?
A: Yes, in some cases, the production possibilities curve can be a straight line. This occurs when the opportunity cost of producing one good remains constant regardless of the production level. However, this is a relatively uncommon scenario. In most realistic situations, the opportunity cost increases as we produce more of one good, leading to a concave curve.
Q: What is the relationship between the production possibilities curve and economic growth?
A: The PPC illustrates economic growth potential. When resources increase or technology improves, the curve shifts outward, expanding the production possibilities frontier and allowing for greater output of both goods. Conversely, a decrease in resources or a decline in technology can cause the curve to shift inward, contracting the possibilities.
Q: Why is the production possibilities curve important for understanding international trade?
A: The PPC helps explain the concept of comparative advantage, which is central to international trade. When countries specialize in producing goods where they have a lower opportunity cost, they can produce more goods overall, resulting in greater efficiency and higher standards of living through international trade.
Creating Production Possibilities Schedules And Curves
Conclusion
Production possibilities schedules and curves provide a powerful framework for understanding the trade-offs inherent in resource allocation and the potential for economic growth. By visualizing these concepts, we gain invaluable insights into how limited resources can be used to maximize societal well-being. Whether you’re a student, a business leader, or simply a curious individual, mastering these tools can enhance your understanding of the economy and empower you to make informed decisions in an ever-changing world.
Are you interested in exploring these concepts further and applying them to real-world economic scenarios? Share your thoughts and questions in the comments below!






