Have you ever wondered what makes up the air you breathe, the water you drink, or even the very ground you stand on? The answer lies in the fascinating realm of chemistry, where the fundamental building blocks of everything around us are known as elements. And at the heart of this world, we find the first 20 elements, a collection of substances that, despite their seemingly simple nature, form the foundation for an incredibly diverse universe.
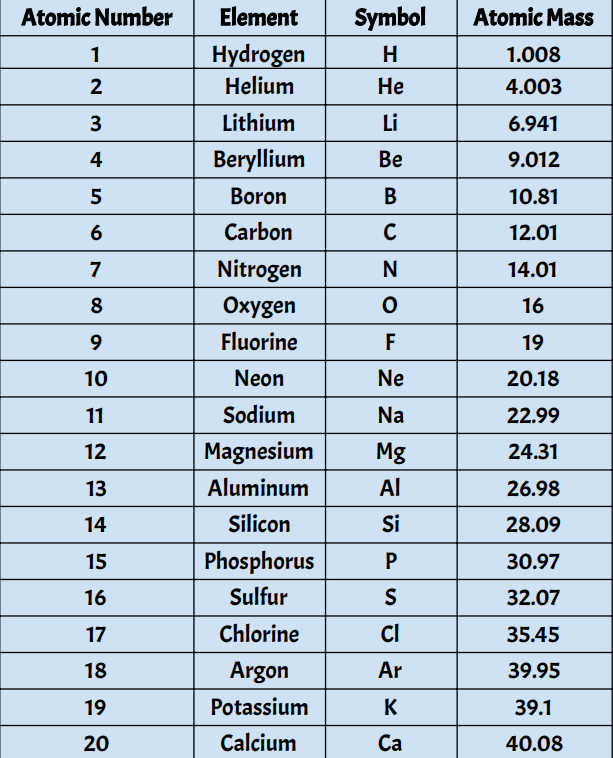
Image: chemistrytalk.org
Today, we embark on a journey to explore these first 20 elements, unraveling their unique properties, uncovering their fascinating history, and understanding their profound impact on our lives. We’ll delve into how these elements form the foundation of everything we know and experience, from the majestic mountains to the intricate workings of our own bodies.
The First 20 Elements: A Symphony of Diversity
From the lightest element, hydrogen, to the heavier, more complex calcium, each of the first 20 elements tells a story. This collection includes some of the most familiar and essential elements on Earth, such as:
- Hydrogen (H), the simplest and most abundant element in the universe, a key component of water and fuels like methane.
- Oxygen (O), the element that allows us to breathe, essential for respiration and combustion.
- Carbon (C), the backbone of life, the foundation for all organic molecules, forming the basis of countless biological processes.
- Nitrogen (N), a vital component of the air we breathe, essential for plant growth and a crucial component of proteins.
The first 20 elements encompass a wide range of properties, each playing a unique role in the natural world and in our technological advancements.
The Power of Atomic Mass: Unveiling the Weights of Elements
At the core of understanding elements lies their atomic mass. Atomic mass is a fundamental property that reflects the total number of protons and neutrons within the nucleus of an atom. It gives us a way to quantify the weight of an element, helping us understand how it behaves and interacts with other elements.
Hydrogen (H), with an atomic mass of approximately 1, is the lightest element. It’s so light that it can easily escape Earth’s gravity, which is why we find vast quantities of hydrogen in space.
Oxygen (O), with an atomic mass of roughly 16, is much heavier than hydrogen. This makes oxygen a vital component of our atmosphere, as its heavier weight helps it stay close to Earth’s surface.
As we move through the first 20 elements, we see a gradual increase in atomic mass. This increase in mass corresponds to an increase in the number of protons and neutrons within the nucleus of each element.
Unveiling the History: A Timeline of Discovery
The discovery of the first 20 elements is a fascinating journey that spans centuries. Some elements, like hydrogen and oxygen, were known to ancient civilizations, while others were discovered through the tireless efforts of scientists in the 18th and 19th centuries.
Hydrogen (H) was first recognized in the 18th century by Henry Cavendish, who observed the production of a flammable gas from the reaction of metals with acids.
Oxygen (O) was independently discovered by Carl Wilhelm Scheele and Joseph Priestley in the 1770s.
Carbon (C) has been known since prehistoric times, with early civilizations using carbon in the form of charcoal and soot.
The discovery of the first 20 elements is a testament to the ingenuity and perseverance of scientists throughout history. Each element’s discovery brought humankind closer to unlocking the secrets of the universe.

Image: mungfali.com
Beyond the First 20: A Universe of Elements
While the first 20 elements hold immense significance, they are just the beginning. Beyond these familiar elements, a vast array of elements await discovery. The periodic table, with its beautifully organized rows and columns, presents a map of the universe’s elements, each with its unique properties and applications.
The first 20 elements form the bedrock of our understanding of chemistry and physics. They are the building blocks of stars, planets, and life itself. Understanding the first 20 elements is like unlocking the foundation upon which our very existence rests.
The Power of Elements: From Technology to Life Itself
The first 20 elements have profoundly impacted our world, driving technological advancements and shaping the very fabric of life.
Silicon (Si) is a crucial element in the electronics industry. Its ability to conduct electricity has revolutionized computing and technology.
Iron (Fe), the backbone of our modern society, is used in construction, transportation, and numerous industrial processes.
Calcium (Ca) is essential for bone and tooth formation, playing a vital role in our health.
The Continual Evolution: New Discoveries and Applications
The world of elements is constantly evolving. Scientists continue to discover new elements, pushing the boundaries of our knowledge. Emerging technologies and applications are constantly being developed, leveraging the unique properties of the first 20 elements and beyond.
Understanding the first 20 elements is not merely knowing their names and properties. It’s about grasping the intricate relationships between elements, their interactions, and their profound impact on our world.
First 20 Elements With Atomic Mass
https://youtube.com/watch?v=s5iLzhs2zBc
From Curiosity to Understanding: A Path Forward
By embarking on this journey through the first 20 elements, we have gained a deeper appreciation for the intricate workings of our world. We’ve learned about the fundamental building blocks of matter, their diverse properties, and their enduring influence on our lives.
The knowledge we’ve gained is just the tip of the iceberg. There’s still so much to discover and explore in the world of elements. We encourage you to continue your journey of discovery, expanding your understanding of the building blocks that make up the universe around us.






