Have you ever wondered how the electricity that powers your home, your workplace, and the very fabric of our modern world gets to you? It’s a journey that starts at power stations, traverses vast distances, and finally arrives at your doorstep. But behind the scenes, a complex web of equipment and infrastructure works tirelessly to keep the lights on. A crucial tool for understanding this intricate network is the single line diagram of a substation.
Image: www.vrogue.co
Imagine you’re standing in the heart of a city, surrounded by towering buildings and bustling streets. Now picture the invisible energy flowing beneath you, powering every light, computer, and appliance. This unseen network is a testament to the ingenuity of electrical engineers, and at the core of this intricate system sits the substation. A substation acts as a crucial intermediary, receiving high-voltage power from transmission lines and transforming it into lower voltages suitable for distribution to homes and industries. The single line diagram is like a blueprint that unveils the secrets of this vital infrastructure, revealing the interconnectedness of its components and the flow of electricity.
Delving into the Essence of Single Line Diagrams
Imagine a blueprint that condenses a complex system into a simplified, yet informative, visual representation. This is the essence of the single line diagram, a powerful tool used by electrical engineers to understand, analyze, and design substations. It’s not a detailed schematic, but rather a visual roadmap of the substation’s key components and their connections, enabling a clear understanding of the electrical flows within the system.
Think of it as a map of a city, where the main arteries are the transmission lines, the smaller streets are the distribution lines, and the buildings are the transformers, circuit breakers, and other vital equipment. Every line on the diagram represents a conductor, and every symbol represents a piece of electrical equipment. The simplicity of the representation lies in its ability to convey the essential information without cluttering the diagram with intricate details.
Key Components of a Single Line Diagram
The single line diagram typically includes:
- Buses: These act as central points within the substation, allowing for the interconnection of different components and facilitating the flow of electricity.
- Transformers: These are the heart of the substation, stepping down the high voltage from transmission lines to lower voltages suitable for distribution.
- Circuit Breakers: These are essential safety devices that can interrupt the flow of electricity in case of faults or overloads.
- Switches: These allow for the control and isolation of different parts of the substation.
- Relays: These are devices that monitor the operation of the substation, initiating protective actions to maintain safety and reliability.
Interpreting the Flow of Power
Each line on the single line diagram represents a conductor, and the thickness of the line may indicate the size of the conductor and the amount of current it can carry. Arrows on the lines can indicate the direction of current flow, crucial for understanding how power is distributed throughout the substation.
The single line diagram acts as a roadmap, guiding you through the intricate pathways of electricity within the substation. By following the lines, you can trace the journey of power from the incoming transmission lines, through the transformers, to the outgoing distribution lines, illuminating the interconnectedness of these vital components.
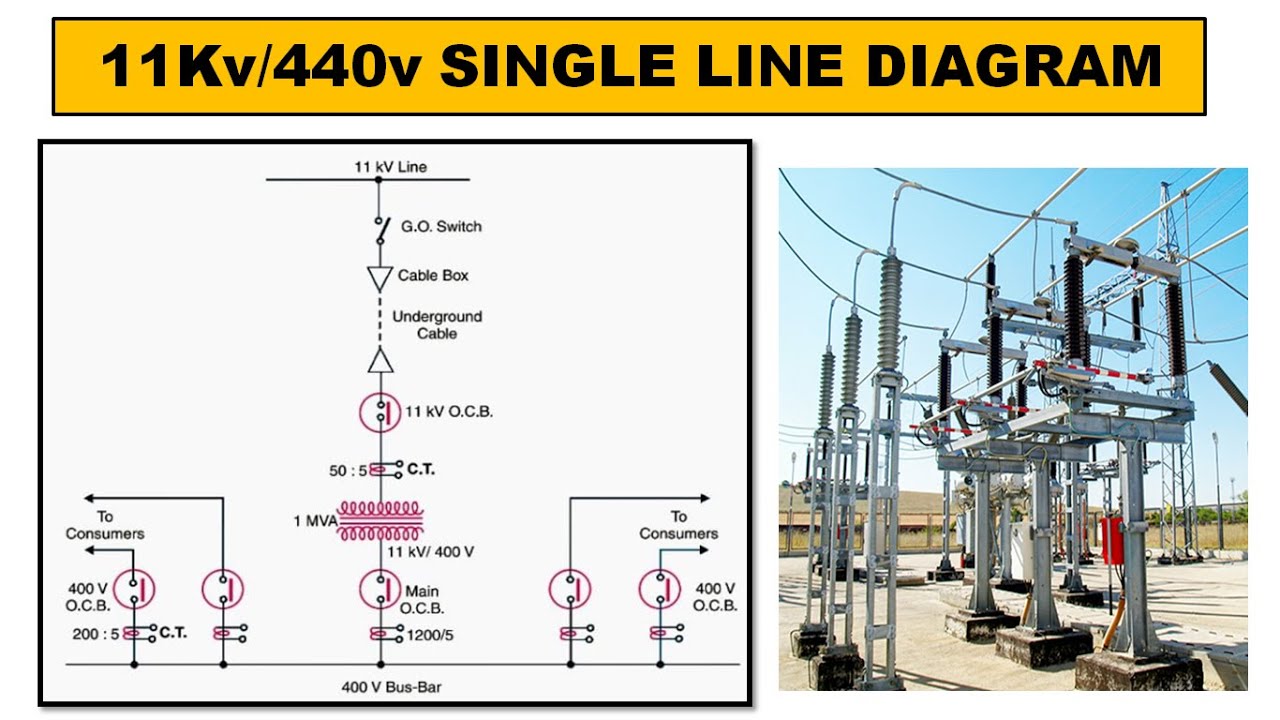
Image: docs.cholonautas.edu.pe
Unveiling the History and Evolution of Single Line Diagrams
The use of single line diagrams dates back to the early days of electrical power systems, a testament to their enduring relevance in the world of electrical engineering. As power systems expanded and became more complex, the need for a standardized means of representation became increasingly apparent. Single line diagrams emerged as a solution, providing a clear and concise way to visualize the interconnectedness of electrical components.
Over the years, single line diagrams have evolved, adapting to the advancements in power systems and the increasing complexity of electrical grids. The introduction of digital software has revolutionized the creation and analysis of diagrams, enabling engineers to create and analyze these diagrams in a more efficient and dynamic way.
Real-World Applications of Single Line Diagrams
The applications of single line diagrams extend far beyond the realm of conceptual understanding. They are essential tools for a wide range of activities within the power industry, including:
- Design and Planning: Engineers use single line diagrams to design and plan new substations, ensuring the efficient integration of components and the optimal flow of electricity.
- Operations and Maintenance: Understanding the intricacies of the substation is crucial for maintaining its proper operation. Single line diagrams help operators to identify and isolate faults, ensuring the safe and reliable delivery of electricity.
- Troubleshooting: In case of power outages or other operational issues, single line diagrams assist in pinpointing the problem area and facilitating swift repairs, minimizing downtime and service disruptions.
- Training: Single line diagrams serve as valuable resources for training personnel involved in the operation and maintenance of substations, allowing them to understand the intricacies of the system and become familiar with the roles of different components.
The Importance of Effective Communication
Beyond their practical applications, single line diagrams are vital tools for effective communication within the power industry. They provide a common visual language that enables engineers, operators, and other stakeholders to understand the complex workings of substations, regardless of their specific expertise.
These diagrams bridge the gap between technical jargon and clear visual representation, ensuring that everyone involved in the operation and management of power systems can contribute effectively and understand the interconnectedness of these crucial infrastructure components.
Exploring the Future of Single Line Diagrams
As power systems continue to evolve, driven by the integration of renewable energy sources and the growing demand for more resilient and efficient grids, single line diagrams must adapt to these changes. The advancement of digital technologies opens up new possibilities, enabling the creation of interactive and dynamic diagrams that integrate real-time data, provide predictive analytics, and enhance communication and collaboration among stakeholders.
The future of single line diagrams lies in their ability to seamlessly integrate with the broader digital landscape of the power industry, contributing to the development of smarter, more responsive, and sustainable power systems.
Single Line Diagram Of A Substation
Key Takeaways and a Call to Action
The single line diagram is a powerful tool, providing a simplified yet comprehensive blueprint of the intricate workings of substations. It’s essential for understanding the flow of power, communicating ideas effectively, and facilitating the safe and reliable operation of these vital infrastructure components.
We encourage you to explore the fascinating world of power systems and the role of single line diagrams in making it all work. By embracing the concepts and applications of these diagrams, you can gain a deeper appreciation for the vital role they play in our daily lives, empowering you to navigate the complexities of the electrical world.






