Have you ever looked at a computer screen and wondered about the intricate components hidden behind the digital canvas? While the screen itself is what we interact with, it’s just one piece of a complex puzzle that brings your digital world to life. Understanding these components is crucial for anyone who wants to navigate the world of PCs with confidence. This guide serves as your comprehensive solution to identifying and understanding the parts of a desktop PC screen, tackling the challenging parts of a desktop PC screen identification worksheet answers.
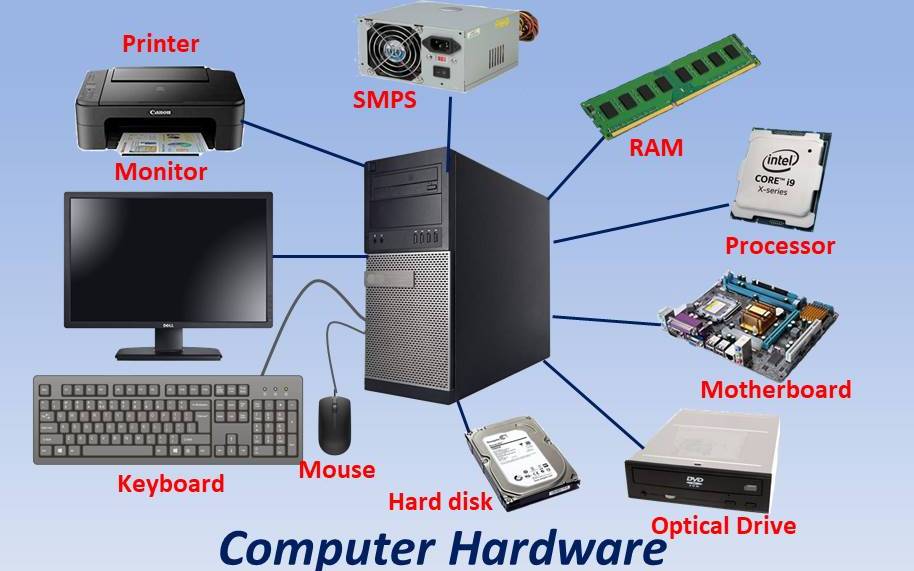
Image: blog.uniquez.co
Beyond the pixels, your screen connects to a web of electronics that transform digital data into the visual images you see. From the humble power cord to the intricate graphics card, each component plays a vital role in how information is displayed. This journey will guide you through the anatomy of your desktop PC screen, breaking down the complexities into digestible chunks.
The Heart of the Display: Understanding the Monitor
The monitor, the most prominent part of the desktop PC screen identification worksheet answers, serves as the window to your digital world, displaying everything from text and images to videos and games. Let’s dissect this key component:
1. Display Panel:
This is the core of the monitor. It’s where the image is created. Typically, you’ll encounter these types:
- LCD (Liquid Crystal Display): This is the most common type found in desktop monitors. LCD panels use liquid crystals to control light passing through them, creating the image.
- LED (Light-Emitting Diode): This type uses LEDs as the backlight, often providing better contrast and color accuracy.
- OLED (Organic Light-Emitting Diode): These panels are newer and offer superior contrast, deeper blacks, and wider viewing angles but are also generally more expensive.
2. Resolution and Aspect Ratio:
Resolution refers to the number of pixels that your monitor can display. Higher resolution means more pixels, resulting in sharper images. Aspect ratio is the ratio of width to height, common examples being 16:9 (wide screen) and 4:3 (traditional aspect ratio).

Image: learningzonefleischer.z1.web.core.windows.net
3. Refresh Rate:
Refresh rate determines how many times the image is redrawn per second, measured in Hertz (Hz). A higher refresh rate reduces motion blur, making gameplay and fast-paced content smoother.
4. Response Time:
Response time refers to how quickly a pixel can change color. This is particularly important for gaming, where faster response times minimize ghosting and blur during fast movement.
Beyond the Display: Connecting the Dots
The monitor is just the final stage of displaying information. Here’s how information travels to the screen:
1. Graphics Card (GPU):
This specialized piece of hardware is the powerhouse behind your display. The graphics card translates data from your CPU into visual output, sending it to your monitor. Higher-end GPUs offer faster performance and better image quality, particularly important for gaming and creative tasks.
2. Cables:
Digital signals travel from your computer to your monitor through cables:
- HDMI (High-Definition Multimedia Interface): Provides high-quality video and audio transmission.
- DisplayPort: Supports higher refresh rates and resolutions, making it ideal for demanding tasks.
- DVI (Digital Visual Interface): Also transmits digital signals, but is being phased out in favor of HDMI and DisplayPort.
- VGA (Video Graphics Array): An older standard often used for legacy devices.
3. The Motherboard:
The motherboard is the central hub of your PC, where all components are interconnected. The graphics card, through a dedicated slot, connects to the motherboard which passes signals to the monitor via cables. This intricate connection ensures smooth and efficient data flow.
The Power Behind the Picture
Every component of your desktop PC screen needs power to function:
1. Power Supply:
The power supply converts household electricity into a usable form for your components, including your monitor.
2. Power Connections:
Each component, including your monitor, uses dedicated power connectors. The power supply provides these connections. Some monitors are powered via USB, which draws power directly from your computer.
Troubleshooting Your Desktop PC Screen
A black screen or a distorted image can be frustrating. Here are some common troubleshooting tips:
- Check the power cables: Ensure both the monitor and computer are plugged in firmly.
- Investigate the cable connection: Try using a different cable, or ensure the current cable is securely connected at both ends.
- Update your graphics drivers: Outdated drivers can cause display problems. Visiting your graphics card manufacturer’s website for the latest drivers is often the solution.
- Adjust monitor settings: Troubleshoot issues like brightness, contrast, or resolution settings within your monitor’s menu.
Parts Of A Desktop Pc Screen Identification Worksheet Answers
https://youtube.com/watch?v=iOtfZFXYD-k
A Digital Window with Infinite Potential
Understanding the parts of your desktop screen is a journey of discovery. From the sleek monitor to the powerful graphics card, each component plays a vital role in bringing your digital experiences to life. This knowledge empowers you to troubleshoot issues and make more informed decisions when upgrading your PC. As you explore the world of PC hardware, remember this: your monitor is not just a screen, it’s a window to endless possibilities.
Share your experiences with identifying the parts of your desktop PC screen in the comments below! Together, let’s celebrate the power and potential of this vital piece of technology.






