Have you ever found yourself staring at a tangled mess of wires connected to an ignition switch, feeling completely lost? That feeling, my friend, is familiar to many who own lawnmowers, generators, or other small engines powered by Briggs & Stratton. Fear not, because in this guide, we’re about to unravel the mystery of the 7 terminal ignition switch diagram, shedding light on its complex wiring and helping you understand how it all works.
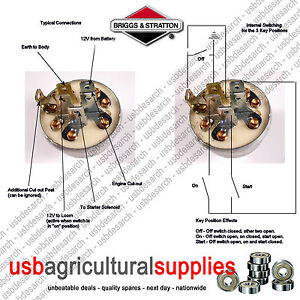
Image: drivenheisenberg.blogspot.com
The 7 terminal ignition switch diagram plays a crucial role in the starting and operation of your engine, acting as a central hub that controls the flow of electricity to various components. Whether you’re a seasoned mechanic or a novice trying to troubleshoot a starting issue, mastering this diagram is essential. So, let’s dive in and unlock the secrets of this vital part of your equipment.
Decoding the 7 Terminal Ignition Switch
The 7 terminal ignition switch isn’t just a random collection of wires and terminals; it’s a carefully designed system that facilitates the engine’s ignition sequence. Think of it as the brain that dictates how electricity flows, ensuring a smooth and controlled start.
Before we delve into the specific terminals, let’s understand the basic functions they perform:
- Ignition Coil (IC): This essential component receives electrical current from the ignition switch, transforming it into high-voltage electricity to spark the spark plug and ignite the fuel.
- Battery (BAT): The battery provides the power source for the entire ignition system.
- Starter Motor (ST): The starter motor is triggered by the ignition switch to crank the engine, initiating the combustion cycle.
- Start (ST): This terminal is engaged when the ignition key is turned to the start position, supplying power to the starter motor.
- Run (RN): When the ignition key is in the run position, this terminal provides power to the ignition coil and other electrical components.
- Ground (GND): This terminal acts as the return path for electricity, completing the electrical circuit and allowing current to flow.
- Accessory (ACC): This terminal provides power to auxiliary components like headlights or other accessories when the ignition key is in the “on” position.
With these basic functions in mind, let’s now examine the wiring diagram in detail.
Understanding the 7 Terminal Wiring Diagram
Visualizing the wiring diagram is crucial to understanding the flow of electricity through the ignition switch. Let’s picture it:
Imagine a small box with seven numbered terminals protruding from it. Each terminal corresponds to one of the components mentioned above. The diagram, often provided in your engine’s manual or easily found online, shows how these terminals are connected to each other and to the various components. It’s like a roadmap showing the path electricity follows.
Now, let’s break down the most common configurations of the 7 terminal ignition switch diagram.
- Terminal 1: Ignition Coil (IC): This terminal receives power from the ignition switch when the key is turned to the “run” position. The power flows to the ignition coil, ultimately igniting the fuel.
- Terminal 2: Battery (BAT): This terminal connects directly to the positive terminal of your battery, ensuring a constant supply of power to the ignition switch.
- Terminal 3: Starter Motor (ST): This terminal is energized when the key is turned to the “start” position, supplying power to the starter motor to crank the engine.
- Terminal 4: Start (ST): This terminal is typically a spring-loaded switch that connects to Terminal 3 only while the ignition key is in the “start” position. This ensures the starter motor only receives power when you’re trying to start the engine.
- Terminal 5: Run (RN): When the key is in the “run” position, Terminal 5 supplies power to components like the ignition coil and other electrical systems.
- Terminal 6: Ground (GND): This terminal provides a return path for electricity, grounding the system to complete the circuit and allow current to flow.
- Terminal 7: Accessory (ACC): This terminal is energized only when the key is in the “on” position, providing power to auxiliary components like headlights and various accessories.
Troubleshooting Ignition Switch Issues
Now that you have a better understanding of the 7 terminal ignition switch diagram, let’s explore how to identify and troubleshoot potential issues.
Common Signs of a Faulty Ignition Switch:
- Engine won’t start.
- Engine runs erratically or shuts off unexpectedly.
- Battery drains quickly when the ignition is off.
- Electrical components malfunction or don’t work at all.
Steps to Troubleshoot a Faulty Ignition Switch:
- Visual Inspection: Start by visually inspecting the ignition switch. Check for any obvious signs of damage like loose wires, corroded terminals, or a broken key switch.
- Continuity Testing: Use a multimeter to check for continuity between the terminals. Refer to the wiring diagram to identify the correct terminals for each component and test if electricity is flowing through the circuit.
- Power Testing: Use the multimeter to test for voltage at the terminals. This helps you determine if the ignition switch is receiving the correct power from the battery.
- Replace the Ignition Switch: If your tests reveal a faulty switch, the best course of action is to replace the ignition switch.

Image: manualdbxavier.z13.web.core.windows.net
Expert Tips for Ignition Switch Maintenance
- Prevent Corrosion: Apply dielectric grease to the terminals and connections to prevent corrosion and ensure smooth electrical flow. This simple maintenance step can significantly extend the lifespan of your ignition switch.
- Regular Inspection: Periodically inspect your ignition switch for any signs of wear and tear. Early detection of issues can prevent potential problems down the line.
- Use the Right Tools: When working on your ignition switch, use high-quality tools designed for the task. Avoid using tools that could damage the delicate electrical components.
Briggs And Stratton 7 Terminal Ignition Switch Diagram
Conclusion
The Briggs and Stratton 7 terminal ignition switch diagram may seem intimidating at first, but armed with this information, you’re now better equipped to understand its intricacies. It’s your guide to unlocking the secrets of your engine’s ignition system. By knowing the role of each terminal and how they connect, you can confidently diagnose and troubleshoot any issues that arise. This knowledge empowers you to keep your equipment running smoothly and enjoy the satisfaction of doing it yourself. So, roll up your sleeves, don your mechanic’s cap, and delve into the world of ignition switches with newfound confidence. Remember, understanding your engine’s system is the key to a world of possibilities.






