Imagine a tiny, bustling city teeming with activity, all confined within a delicate, flexible wall. This is the incredible world of a cell, the fundamental unit of life. And guarding the entrance to this miniature metropolis, ensuring the flow of essential materials and the exclusion of harmful intruders, is the cell membrane. This remarkable structure, like a sophisticated gatekeeper, plays a crucial role in keeping the cell alive and functioning. To understand the intricacies of this vital barrier, scientists have devised a simple yet powerful experiment: the cell membrane bubble lab. Let’s delve into this experiment, unraveling the mysteries of the cell membrane and discovering its vital role in the grand tapestry of life.

Image: myans.bhantedhammika.net
The cell membrane bubble lab is a captivating hands-on activity that vividly illustrates the structure and function of the cell membrane in a fun and engaging way. Through this experiment, you’ll create miniature versions of cell membranes using common household materials. The process involves a simple mixture of dish soap, water, and glycerin, which, when blown into bubbles, resembles the phospholipid bilayer that forms the foundation of the cell membrane. This intuitive approach allows us to visualize how this vital barrier functions to protect and regulate the cell’s environment. By witnessing firsthand the creation and interaction of these miniature cell membranes, you’ll gain a deeper understanding of the complex processes occurring within every living organism.
A Deeper Look: Deconstructing the Cell Membrane Bubble Lab
The cell membrane bubble lab is a brilliant example of how scientific explorations can be simplified and made accessible to everyone. This experiment serves as a stepping stone to comprehending the dynamic nature of the cell membrane, a structure that plays an essential role in various biological processes. Let’s dissect the key elements of this lab to gain a deeper appreciation for the science behind the beautiful bubbles.
Ingredients for the Experiment:
The cell membrane bubble lab requires a few simple everyday ingredients. These include:
-
Dish Soap: The dish soap is a crucial component of the cell membrane bubble lab. It acts as a surfactant, reducing the surface tension of water. This allows the soap molecules to form a thin film, which essentially mimics the phospholipid bilayer of the cell membrane.
-
Water: Water serves as the solvent in this experiment. It dissolves the soap molecules, forming a solution that can then be blown into bubbles.
-
Glycerin: Glycerin, a thick, syrupy liquid, adds viscosity to the solution, making the bubbles more durable and resistant to bursting.
Constructing the Cell Membrane Analogy:
The magic of this experiment lies in its ability to showcase the cell membrane’s structure and function through a simple analogy. The thin bubble film formed by the soap solution represents the phospholipid bilayer of the cell membrane. This bilayer is comprised of two layers of phospholipid molecules, each with a hydrophilic (water-loving) head and a hydrophobic (water-fearing) tail. The hydrophilic heads face outward, interacting with the watery environment both inside and outside the cell, while the hydrophobic tails face inward, forming a barrier against water.
The “Gatekeepers” of the Cell:
The cell membrane isn’t just a passive barrier; it’s a bustling gateway, controlling the passage of substances into and out of the cell. This selective permeability is crucial for the cell’s survival. Think of the bubble as a miniature cell, and the air inside represents the cell’s internal environment. When you blow air into the bubble, it expands, demonstrating how the cell membrane allows the passage of essential molecules like nutrients and oxygen into the cell.
The “Keep Out” Signs:
The cell membrane also acts as a security guard, keeping harmful substances out. Think of the bubble’s film as the cell membrane. If you try to poke the bubble with a sharp object, it pops, symbolizing how the cell membrane protects against harmful agents that could disrupt its internal environment.
Exploring the Membrane’s Dynamic Nature:
Cells are dynamic entities, constantly adapting to their surroundings. The cell membrane, like a flexible wall, readily adapts to these changes. In our bubble analogy, you can observe this flexibility by gently pressing on the bubble, causing it to deform. This illustrates how the cell membrane can adjust its shape to accommodate its internal environment.
The “Gatekeeping” Mechanism:
The cell membrane’s selectivity arises from various specialized proteins embedded within its phospholipid bilayer. These proteins act as “gatekeepers,” facilitating the movement of specific substances across the membrane, while blocking others. While we can’t visualize these proteins in the bubble lab, they are essential to the functioning of the cell membrane.
Cell Membrane’s Essential Roles:
The cell membrane’s intricate structure and function are essential for the survival of every living organism. Here’s a peek into some of its vital roles:
-
Cellular Communication: The cell membrane acts as a communication center, receiving and relaying messages from other cells and the environment. This communication is crucial for coordinating cellular activities and maintaining the body’s overall health.
-
Transport of Nutrients and Waste: The cell membrane controls the passage of nutrients, oxygen, and essential molecules into the cell. It also eliminates waste products, ensuring a clean and efficient cellular environment.
-
Protection Against Harmful Agents: The cell membrane acts as a barrier, protecting the cell from harmful substances like toxins and pathogens. This defense mechanism is vital for maintaining cellular integrity and preventing disease.
Expanding Our Understanding:
The cell membrane bubble lab is a simple yet powerful tool for learning about the complexity of cell membranes. It allows us to understand the basic principles of its structure and function while fostering curiosity and excitement for the world of science. By engaging in hands-on experiments like this, we can bridge the gap between abstract concepts and real-world applications, nurturing a deeper appreciation for the wonders of the biological world.
The Cell Membrane Bubble Lab: A Stepping Stone to Understanding Life
The cell membrane bubble lab is more than just a fun experiment; it’s a gateway to comprehending the fundamental principles of life. By grasping the structure and function of the cell membrane, we unlock a deeper understanding of cellular processes, ultimately appreciating the intricate symphony of life. This experiment serves as a springboard for further exploration, encouraging you to delve deeper into the fascinating world of cell biology.
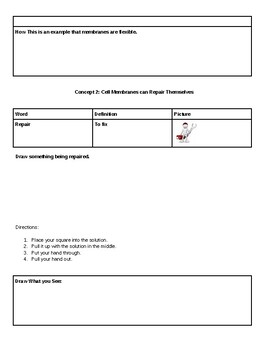
Image: www.teacherspayteachers.com
Cell Membrane Bubble Lab Answer Key
Let’s delve further into the intricate complexity of cell membranes:
-
The phospholipid bilayer is the foundation of the cell membrane. However, it’s not a static structure. It’s highly dynamic, constantly shifting and rearranging, allowing for flexibility and adaptability.
-
Specialized proteins embedded within the phospholipid bilayer play a crucial role in the cell’s communication and nutrient transport. These proteins act as channels, pumps, and receptors, facilitating the movement of molecules across the membrane.
-
The cell membrane is involved in a wide range of essential cellular processes, including cell signaling, cellular recognition, and immune responses. Understanding these processes helps us to grasp the intricate workings of the body and its ability to heal and defend itself.
-
The cell membrane is a target for many drugs and therapies. Understanding its structure and function is essential for the development of new and effective treatments for diseases.
The cell membrane bubble lab, while seemingly simple, sparks a world of scientific exploration. It’s a reminder that even the smallest units of life hold complex wonders that we can unravel through curiosity, experimentation, and an appreciation for the interconnectedness of all living things.






