Imagine a bustling city, a symphony of activity where everything is organized and runs like clockwork. Now imagine that same city suddenly falling into chaos, with buildings collapsing and traffic spiraling out of control. This is what happens when the delicate balance of the cell cycle, the intricate dance of life that governs how cells grow and divide, goes awry. And it’s in this chaotic landscape that cancer emerges, a relentless force that threatens our very existence.

Image: www.coursehero.com
This is where the Howard Hughes Medical Institute (HHMI) steps in, a beacon of hope in the battle against cancer. HHMI scientists, driven by a profound curiosity and a deep desire to alleviate human suffering, have dedicated themselves to decoding the complex mechanisms of the cell cycle and uncovering the secrets behind its dysregulation in cancer. Their research, spanning decades and encompassing a diverse range of disciplines, has yielded a treasure trove of knowledge, transforming our understanding of cancer and paving the way for new and innovative treatments.
The Cell Cycle: A Symphony of Life
Every living organism, from the simplest bacterium to the most complex human being, is built from a fundamental unit: the cell. These tiny factories of life, teeming with complex machinery, are constantly working to sustain our existence. One of the most critical and tightly regulated processes within a cell is the cell cycle, a carefully orchestrated sequence of events that ensures the faithful replication of DNA and the division of a cell into two identical daughter cells.
The cell cycle is like a carefully choreographed ballet, divided into four distinct phases:
- G1 (Gap 1) Phase: The cell grows and synthesizes proteins, gearing up for the next stage.
- S (Synthesis) Phase: The cell replicates its DNA, creating an exact copy of its genetic material.
- G2 (Gap 2) Phase: The cell continues to grow and synthesize proteins, preparing for division.
- M (Mitosis) Phase: The cell divides its duplicated chromosomes, splitting into two identical daughter cells.
This intricate cycle is controlled by a complex network of proteins, acting like the conductor of an orchestra, ensuring each phase proceeds in the right order and at the right time. The proper functioning of the cell cycle is essential for maintaining healthy tissue growth and repair. However, when this delicate balance is disrupted, catastrophic consequences can ensue.
Cancer: A Disruption of the Cell Cycle’s Harmony
Cancer is a disease characterized by uncontrolled cell growth and division, invading and destroying surrounding tissues. At its core, cancer arises from errors in the cell cycle, causing cells to multiply uncontrollably, ignoring the signals that normally regulate their growth. These errors can be caused by a multitude of factors, including:
- Mutations in Genes Controlling the Cell Cycle: Just like a conductor missing a cue, mutations in genes that regulate the cell cycle can cause cells to ignore checkpoints and divide uncontrollably. Some of these genes, known as tumor suppressor genes, act as brakes on cell growth. Others, known as proto-oncogenes, act as accelerators, promoting cell division. Mutations can turn tumor suppressor genes off and proto-oncogenes on, leading to uncontrolled growth.
- External Factors: Exposure to certain chemicals, radiation, and even viruses can damage DNA, causing mutations that disrupt cell cycle regulation. These mutations can create a permissive environment for cells to grow out of control.
HHMI’s Groundbreaking Contributions
HHMI scientists have made significant contributions to our understanding of the cell cycle and its role in cancer development. Their research has not only unveiled the fundamental mechanisms governing cell division but also identified key players in the development of cancer:
-
Cyclins and Cyclin-Dependent Kinases (CDKs): One of the most significant discoveries was the identification of cyclins and CDKs, proteins that act as master regulators of the cell cycle. Cyclins, fluctuating in their levels throughout the cell cycle, bind to CDKs, activating them to control the progression of different phases. HHMI researchers have elucidated the precise roles of different cyclins and CDKs in regulating cell cycle progression, providing a framework for understanding how their dysregulation can lead to cancer.
-
Checkpoint Control: HHMI scientists have also made significant breakthroughs in understanding checkpoints, critical surveillance mechanisms that ensure the cell cycle proceeds correctly. These checkpoints monitor DNA replication and repair, ensuring errors are corrected before cells divide. Mutations in checkpoint genes can lead to the accumulation of errors, increasing the risk of cancer development.
-
The p53 Pathway: The p53 protein is a master tumor suppressor, acting as a guardian of the genome, preventing cells with damaged DNA from dividing. HHMI research has revealed the critical role of p53 in responding to DNA damage, activating pathways that either repair the damage or induce cell death, preventing the propagation of damaged cells. Mutations in p53, found in over 50% of human cancers, are associated with increased cancer risk.
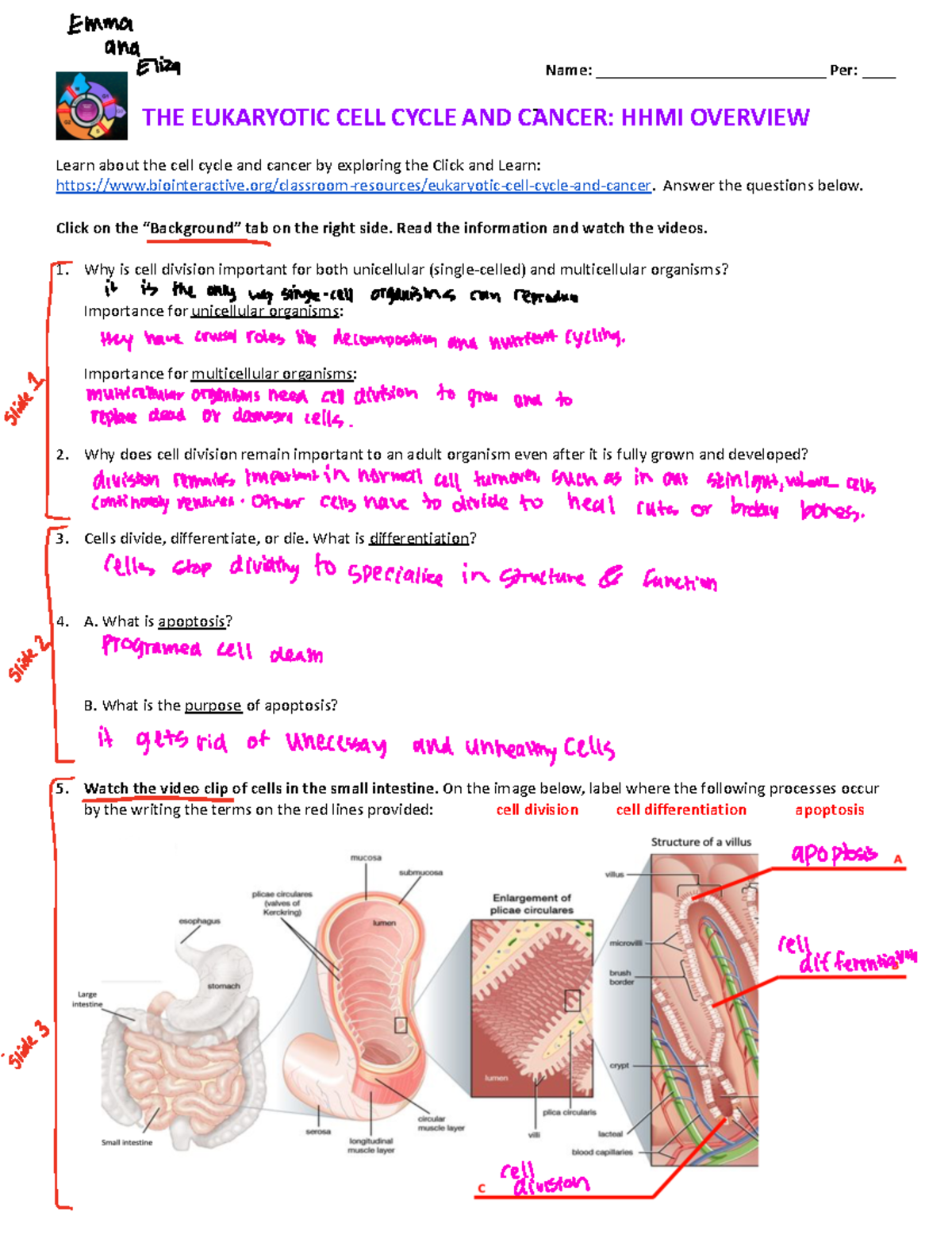
Image: www.studocu.com
Moving Forward: A Future of Innovation
The insights generated by HHMI research have revolutionized our understanding of the cell cycle and its role in cancer. This knowledge has paved the way for new therapeutic strategies aimed at targeting specific components of the cell cycle, disrupting the cancer’s ability to replicate and grow.
The future holds immense promise for new and innovative cancer treatments inspired by HHMI’s pioneering discoveries. Scientists are diligently working on:
- Targeting Specific Cell Cycle Regulators: New drugs are being developed to inhibit the activity of specific cyclin-CDK complexes, preventing the cell cycle from progressing at critical points in cancer cell growth.
- Restoring Checkpoint Function: Efforts are underway to develop therapies that can reactivate checkpoint pathways, enabling cells to detect and correct DNA damage before it leads to uncontrolled growth.
- Exploiting the p53 Pathway: Researchers are exploring ways to re-activate the p53 pathway in cancer cells, restoring its tumor suppressor function and inhibiting cancer growth.
Hhmi Eukaryotic Cell Cycle And Cancer Answers
Empowering Your Health: Key Takeaways
The intricate dance of the cell cycle is a fundamental process for life, and its disruption can lead to the devastating disease of cancer. HHMI research has been instrumental in uncovering the secrets of the cell cycle, shedding light on the mechanisms behind cancer development. This knowledge has spurred the development of new and innovative therapies, offering hope for a future where cancer is no longer a death sentence.
Understanding the cell cycle and the role it plays in cancer empowers us to make informed decisions about our health. Making healthy lifestyle choices that reduce our exposure to cancer-causing agents, embracing preventive screenings, and supporting ongoing research are crucial steps we can take to fight this formidable disease. HHMI’s commitment to cutting-edge research serves as a beacon of hope, illuminating a path toward a world free from the shadow of cancer.






