Remember those childhood trips to the zoo, where you marveled at the variety of animals, each playing a unique role? Did you ever wonder how these creatures were all connected? Behind the scenes, an intricate web of relationships, called a food web, governs the lives of all living things. This web, fueled by the sun’s energy, determines who eats whom and defines the flow of energy within an ecosystem. As we delve into the realm of food webs and energy pyramids, we’ll uncover the secrets of this delicate balance and how it impacts our planet.
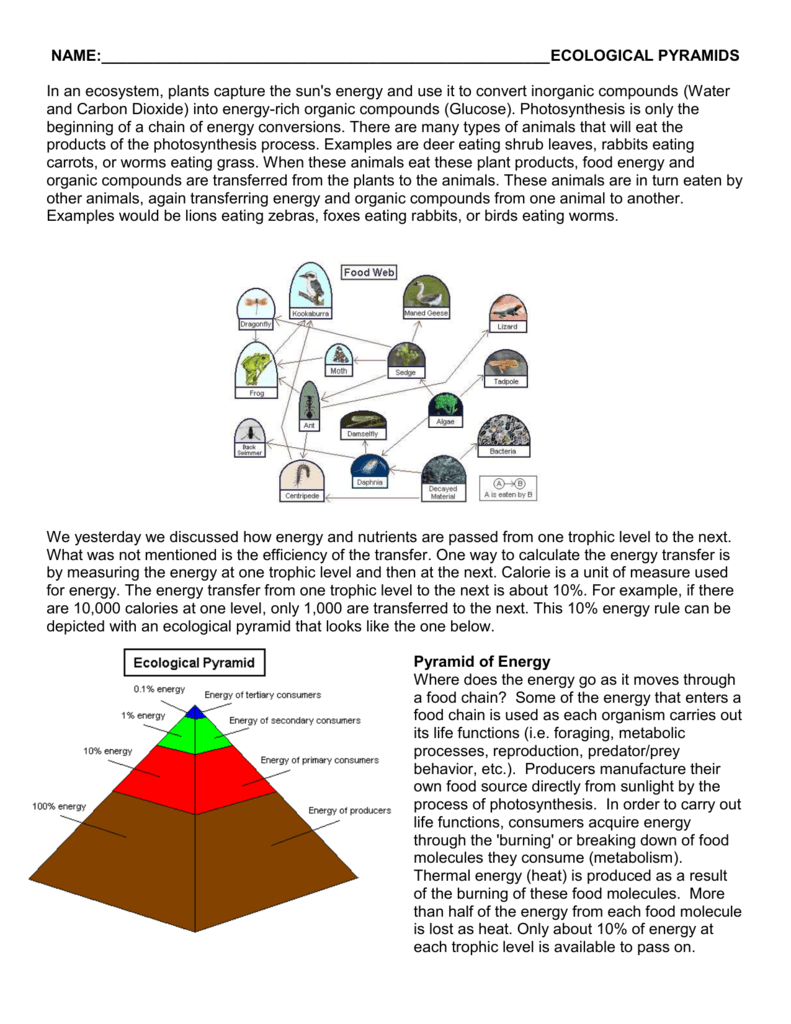
Image: wordworksheet.com
Ever noticed how a simple act like catching a fish can have ripple effects throughout an entire ecosystem? That’s the beauty of food webs – every organism plays a critical role. Through worksheets focused on food webs and energy pyramids, we gain a deeper understanding of these intricate relationships, how energy flows from producers to consumers, and the ecological consequences of disrupting this delicate balance.
Understanding Food Webs and Energy Pyramids
Food webs are like interconnected food chains, illustrating the complex feeding relationships among organisms in an ecosystem. Think of a tangled knot – each thread represents an organism, and how one is connected to the next through feeding. Imagine a meadow; there you have grass (producers), rabbits (primary consumers), foxes (secondary consumers), and even owls (tertiary consumers), all linked together in a food web. This web is a dynamic system, constantly adapting to changes in the environment.
Within this web, energy flows from one organism to the next; this is where energy pyramids come in. Energy pyramids depict the transfer of energy through trophic levels, starting with producers at the base and progressing through primary consumers, secondary consumers, and so on. However, with each transfer, a significant amount of energy is lost as heat. This means that the higher you climb the pyramid, the less energy is available. Therefore, there’s a larger population of producers compared to top predators.
The Importance of Food Webs and Energy Pyramids
Understanding food webs and energy pyramids is essential for several reasons. First, they help us recognize the interconnectedness of life. Every organism, whether a tiny insect or a majestic lion, plays a vital role in the delicate balance of nature. Second, they can be used to predict the impact of changes to an ecosystem. For example, if a disease decimates a population of rabbits, it will likely affect the population of foxes that prey on them. Finally, by studying these concepts, we can gain insights into how to manage and protect our environment more effectively.
Food Webs and Energy Pyramids Worksheets: A Deeper Dive
Food webs and energy pyramids worksheets provide an excellent tool for students to learn and visualize these complex ecological concepts. These worksheets typically offer scenarios involving various organisms in an ecosystem and require students to identify the producers, consumers, and decomposers. They also ask students to create food chains and energy pyramids based on the given information, while integrating critical thinking questions to assess their understanding of energy transfer and the impact of changes within the ecosystem.
Consider this: a worksheet may depict a forest ecosystem with various animals like squirrels, deer, hawks, and fungi. Students would need to identify which of these are producers (fungi), primary consumers (squirrels and deer), and secondary consumers (hawks). Drawing a food web connecting these organisms would illustrate the flow of energy from producers to consumers. Furthermore, students could create an energy pyramid, representing the decreasing amounts of energy available at each trophic level. The worksheet might then present a scenario where the deer population declines due to a disease. Students would be asked to analyze the potential impact on other organisms in the food web, demonstrating their understanding of the interconnectedness of the ecosystem and the consequences of disrupting the balance.

Image: laney-lee.com
Decoding the Answer Key: Unveiling Insights
The answer key for these worksheets is crucial for both teachers and students. It provides a comprehensive guide to ensure understanding and identify areas for improvement. It provides solutions to the food webs and energy pyramids, showing the correct classification of organisms, energy flow, and trophic levels. Moreover, it offers detailed explanations for each answer, highlighting the key ecological concepts and principles. By comparing their answers to the key, students gain a deeper understanding of the concepts and correct any misconceptions.
Unlocking Knowledge: Tips and Expert Advice
To make the most of food webs and energy pyramids worksheets, here are a few tips:
- Visualize the Connections: Draw simple diagrams or use real-life examples to represent food webs and energy pyramids. Visualizing the connections between organisms can make these concepts more tangible and memorable.
- Engage in Role-playing: Allow students to role-play different organisms in a food web, simulating interactions and energy transfer. This hands-on approach can foster understanding through active participation.
- Explore Real-world Examples: Introduce students to real-world cases of food web disruptions, such as invasive species or habitat loss, to demonstrate the consequences of ecological imbalances.
Remember, food webs and energy pyramids are not just abstract concepts. They’re vital for understanding the complex and interconnected nature of our planet. By engaging students with worksheets, we empower them to become stewards of our environment and appreciate the delicate balance that sustains life on Earth.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Why are food webs considered more accurate than food chains?
A: Food webs are more accurate than food chains because they depict the complex and interconnected feeding relationships between multiple organisms in an ecosystem. Food chains, on the other hand, represent a single linear pathway of energy transfer. Realistically, organisms consume a variety of food sources, which makes the food web a more accurate representation of the true feeding interactions within a community.
Q: What is the role of decomposers in food webs?
A: Decomposers are essential for the breakdown of dead organisms and waste products. They recycle nutrients back into the environment, making them available for producers. Without decomposers, ecosystems would become choked with organic matter, preventing the circulation of nutrients and disrupting the delicate balance.
Q: How do changes in one level of a food web impact other levels?
A: Any change in one level of a food web can have ripple effects on other levels. For example, if the population of a primary consumer drops, it can lead to a decrease in the population of secondary consumers that rely on them for food. Conversely, an increase in the population of producers could lead to an increase in the population of primary consumers. Understanding these relationships is crucial for predicting and managing ecological changes.
Q: Can you give an example of a food web in an aquatic ecosystem?
A: In a pond ecosystem, the food web might involve phytoplankton (producers), zooplankton (primary consumers), small fish (secondary consumers), larger fish (tertiary consumers), and birds of prey (top predators). Decomposers like bacteria and fungi play a vital role in breaking down dead organisms and waste, releasing nutrients back into the water for reuse.
Q: Is there a limit to the number of trophic levels in a food web?
A: No, there isn’t a hard limit to the number of trophic levels in a food web. However, the number of levels is typically limited by the loss of energy at each transfer. With each level, about 90% of energy is lost as heat, leading to less energy available for higher trophic levels. Therefore, food webs often have four or five levels, with fewer organisms at higher levels.
Food Webs And Energy Pyramids Worksheet Answer Key
Conclusion
Food webs and energy pyramids are crucial concepts for understanding the interconnectedness of life. From producers to consumers, each organism plays a critical role in the delicate balance of ecosystems. Learning about these concepts through worksheets and answer keys can empower us to become more responsible caretakers of our environment. Are you interested in learning more about the fascinating world of food webs and energy pyramids, and how these concepts impact our lives?






