Ever found yourself staring at a bewildering array of fuses and wondering which one controls your headlights or radio? Navigating the fuse box in your 2002 Honda Civic can feel like deciphering ancient hieroglyphics, but it needn’t be a mystery. This article serves as your guide to understanding the 02 Honda Civic fuse box diagram, demystifying its intricacies and empowering you to tackle electrical issues with confidence.

Image: mydiagram.online
The fuse box, a vital component of your car’s electrical system, acts as a shield, protecting sensitive circuits from damage due to overloads. Its intricate network of fuses is precisely designed to isolate specific circuits, preventing a single electrical fault from crippling your entire vehicle. Understanding this system is crucial for any DIY mechanic, allowing you to diagnose and resolve common electrical problems before they escalate.
Locating the Fuse Box
Before delving into the diagram, it’s essential to know where to find the fuse box in your 2002 Honda Civic. There are two main fuse boxes: the under-hood fuse box, located beneath the hood near the battery, and the interior fuse box, typically situated in the driver’s side dashboard. Both boxes contain diagrams with labels that identify each fuse and its corresponding circuit.
Decoding the Fuse Box Diagram
The 02 Honda Civic fuse box diagram is a visual map that links each fuse to the specific electrical circuit it protects. Understanding this diagram is akin to holding the key to your car’s electrical labyrinth. Each fuse is represented by a numbered circle, with a legend listing the corresponding circuit for each number. This diagram is usually found within the fuse box lid or attached near it.
Interpreting the Fuse Box Diagram
The diagram is relatively straightforward to interpret once you understand the basics.
Let’s break it down:
- Fuse Number: This number corresponds to the fuse’s physical position within the fuse box.
- Circuit Name: This describes the electrical component or function controlled by that specific fuse. It may include terms like headlights, power windows, or radio.
- Amperage Rating: This indicates the maximum current that the fuse can safely handle before blowing. The higher the amperage, the greater the current it can handle.
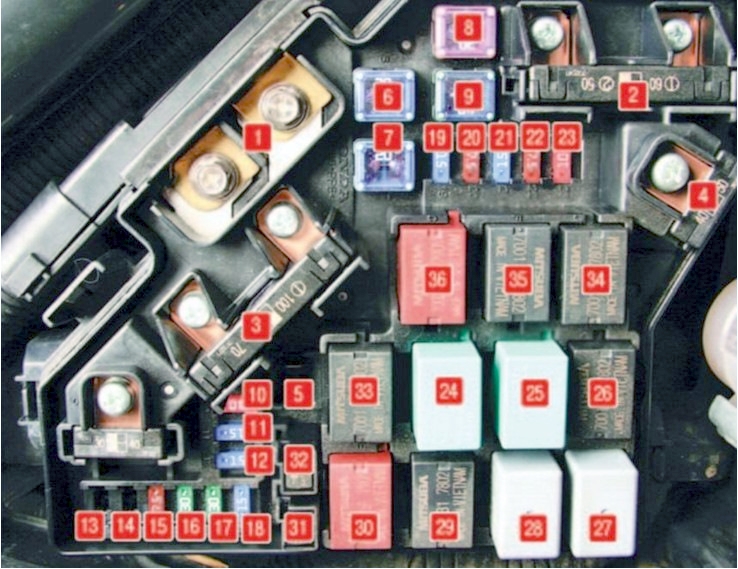
Image: www.176iot.com
Troubleshooting Electrical Issues with the Fuse Box
Once you’ve familiarized yourself with the fuse box diagram, you can use it to diagnose and resolve common electrical issues. Here’s a step-by-step approach for tackling electrical problems:
- Identify the Affected Circuit: Start by determining which electrical component isn’t working. For example, if your headlights are out, you’ll be focusing on the headlight circuit.
- Locate the Corresponding Fuse: Consult the fuse box diagram to find the fuse that protects the affected circuit. Note the fuse number and its amperage rating.
- Inspect the Fuse: Visually inspect the fuse. Look for a blown fuse, indicated by a broken filament or a gap in the metal strip.
- Replace the Fuse: If the fuse is blown, replace it with a fuse of the same amperage rating. Be cautious, as using a higher amperage fuse can lead to further damage.
- Test the Circuit: After replacing the fuse, test the affected circuit to see if the problem is resolved. If the issue persists, the problem may lie beyond the fuse itself.
Common Electrical Problems and Their Corresponding Fuses
Here are some common electrical problems in the 2002 Honda Civic, along with their corresponding fuses, to guide your troubleshooting:
- Headlights: Check fuses 15 (low beam), 16 (high beam) and 17 (fog lights) in the under-hood fuse box.
- Tail Lights: Inspect fuses 4 and 8 (taillights), 3 (brake lights), and 7 (turn signals) in the under-hood fuse box.
- Dashboard Lights: Check fuses 27 (instrument panel lights), 21 (clock) and 24 (gauge cluster) in the interior fuse box.
- Power Windows: Investigate fuses 10 (left front window), 12 (right front window), 9 (left rear window), and 11 (right rear window) in the interior fuse box.
- Radio: Examine fuse 14 (radio) in the under-hood fuse box.
Safety Precautions When Working with Electrical Systems
When working with electrical systems, safety is paramount. Remember these precautions:
- Disconnect the Battery: Always disconnect the negative battery terminal before working on electrical components. This prevents unintended shocks and short circuits.
- Use Insulated Tools: Employ insulated screwdrivers and pliers to avoid electrical contact.
- Be Mindful of Water and Moisture: Never touch electrical components or fuses with wet hands or in wet conditions.
Beyond the Fuse Box
While a blown fuse is often the culprit behind electrical issues, it’s crucial to understand that a problem may go deeper than a simple fuse replacement. If an electrical problem persists despite replacing a fuse, the issue might lie within a wiring harness, a faulty switch, or a malfunctioning electrical component.
02 Honda Civic Fuse Box Diagram
Conclusion
Mastering the art of deciphering your 02 Honda Civic’s fuse box diagram opens doors to electrical troubleshooting confidence. By understanding the diagram and following the steps outlined in this article, you are empowered to address common electrical issues within your car. Remember, safety is key, and if in doubt, always consult a qualified mechanic. Happy troubleshooting!






